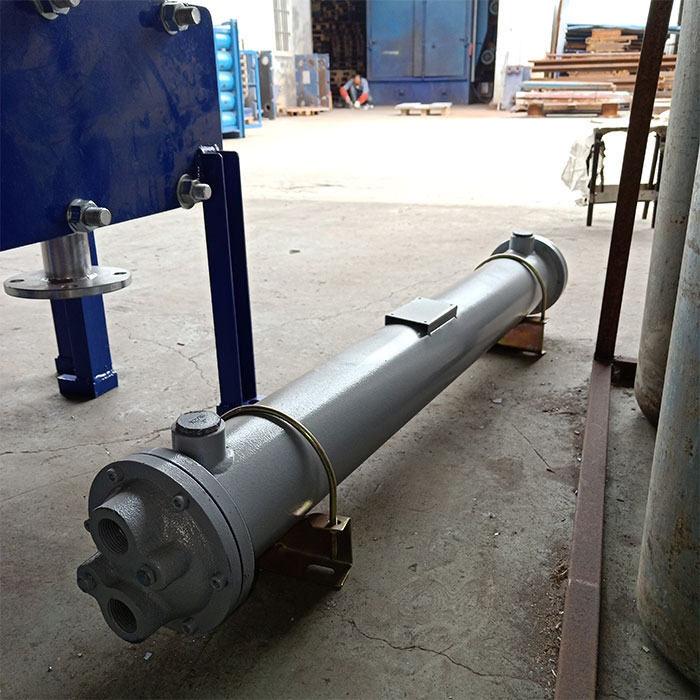
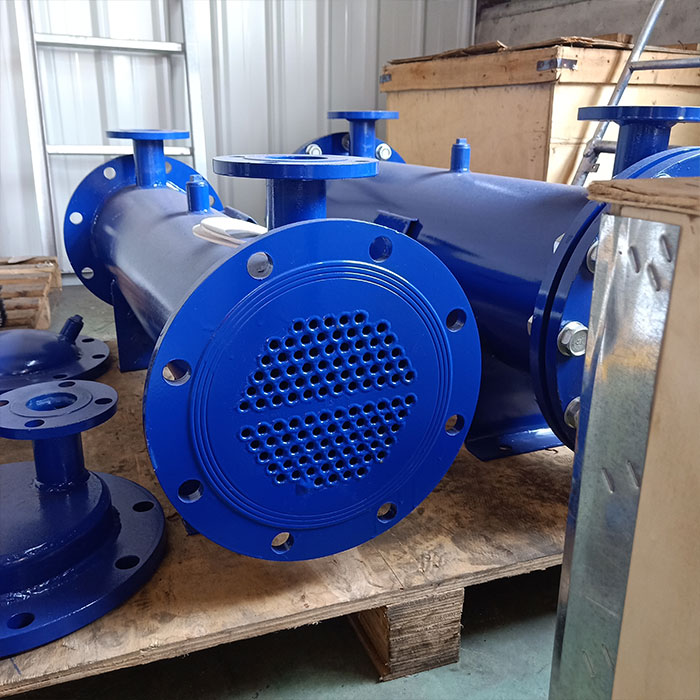
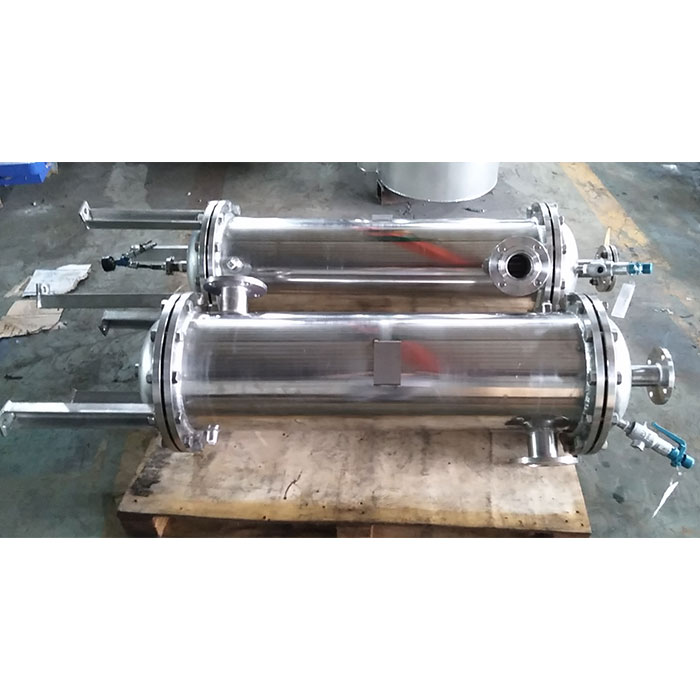
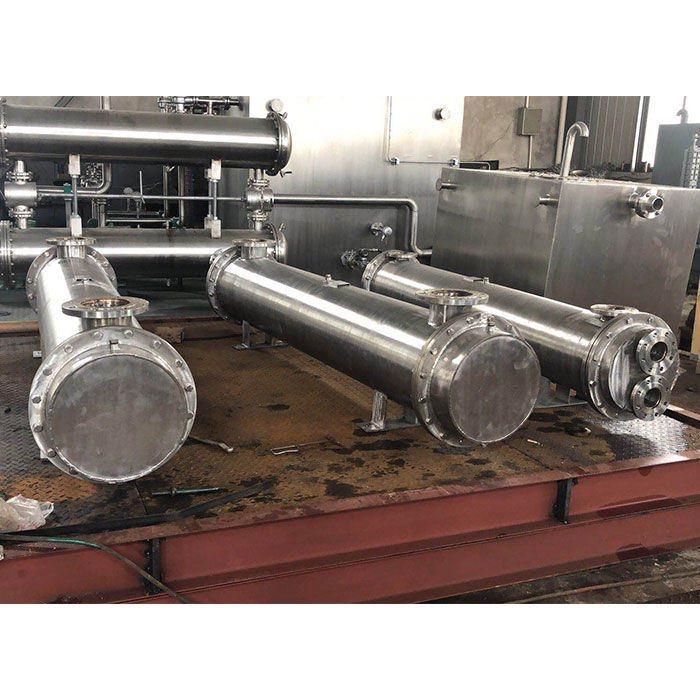
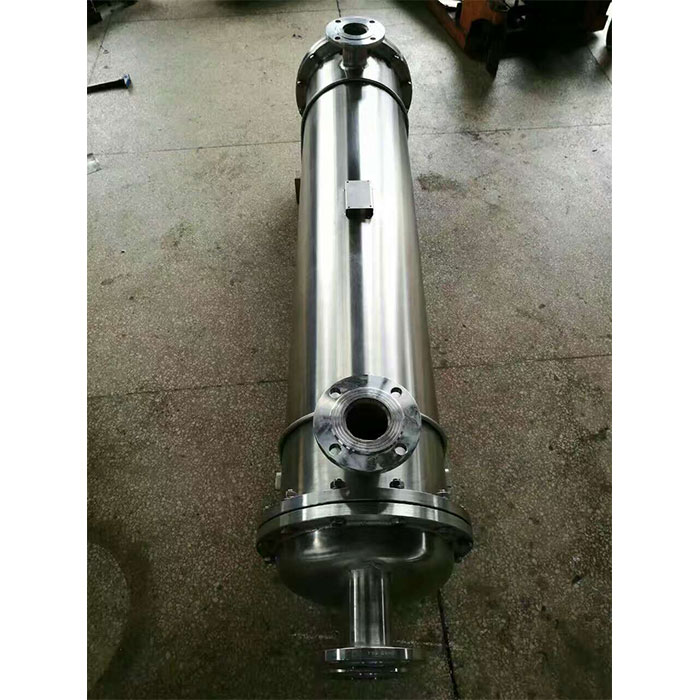
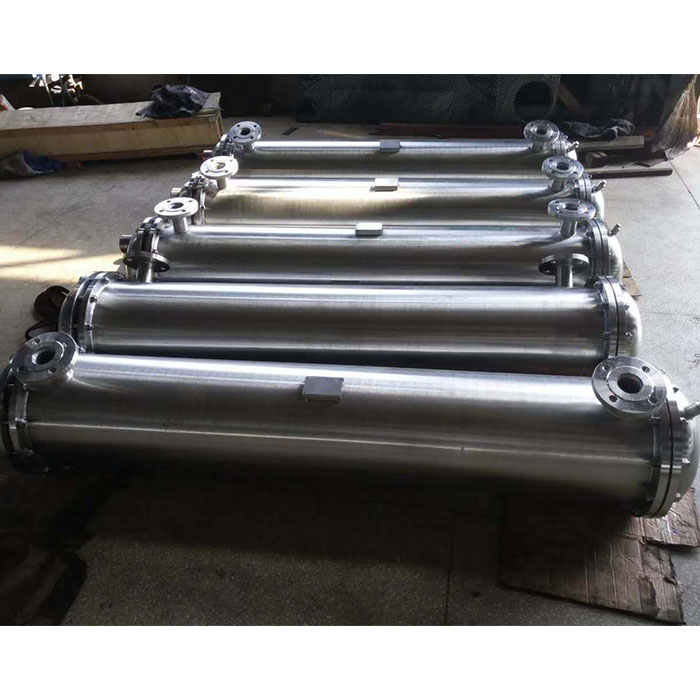
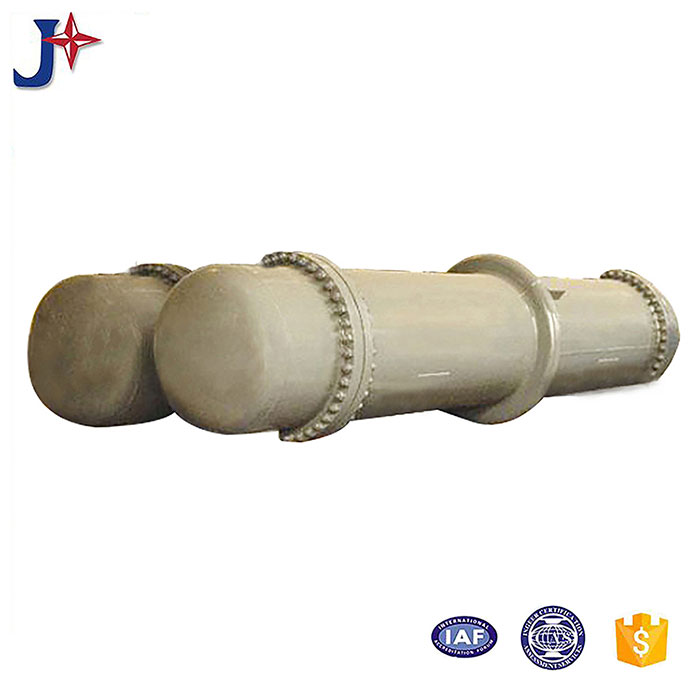
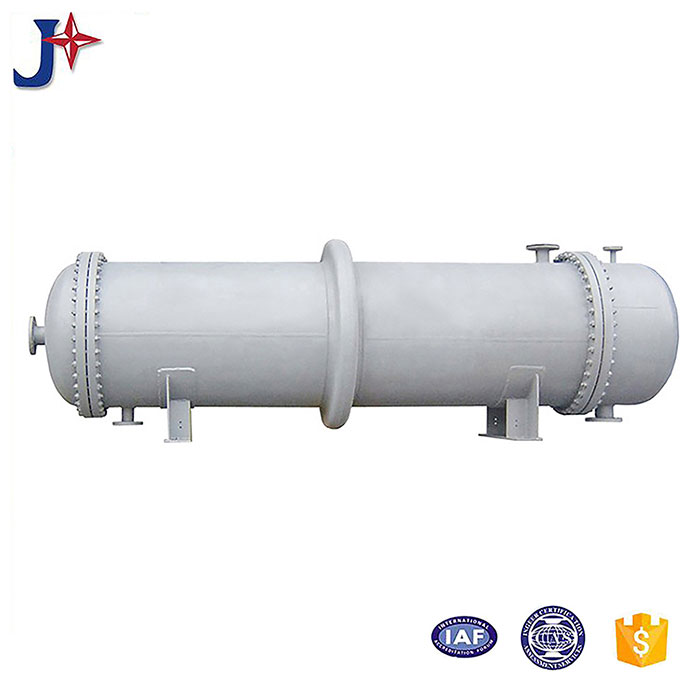
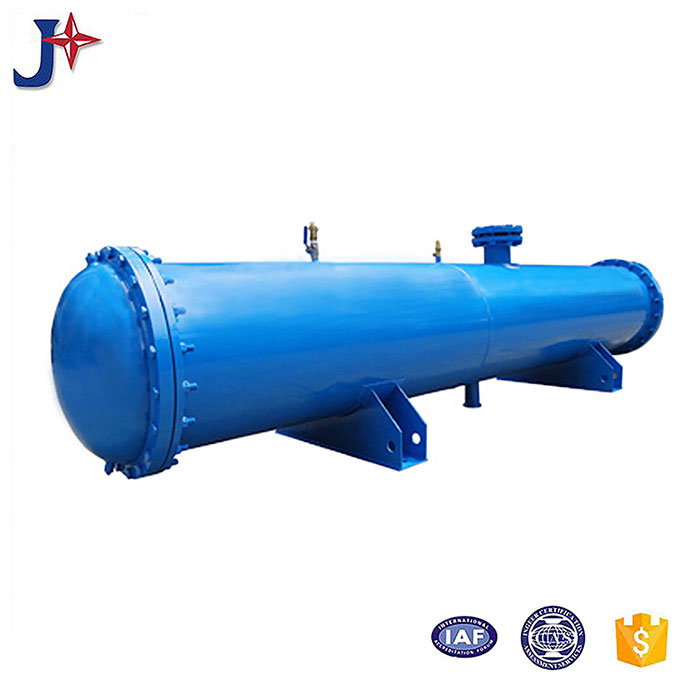
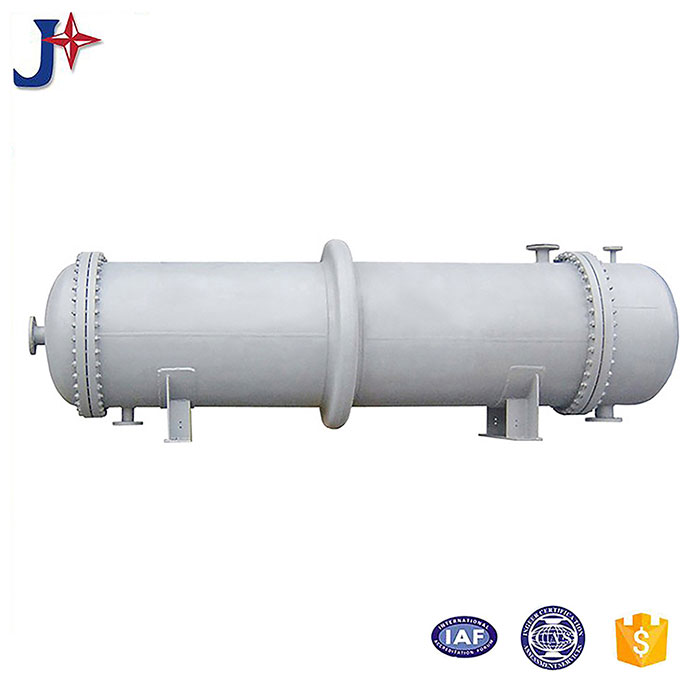
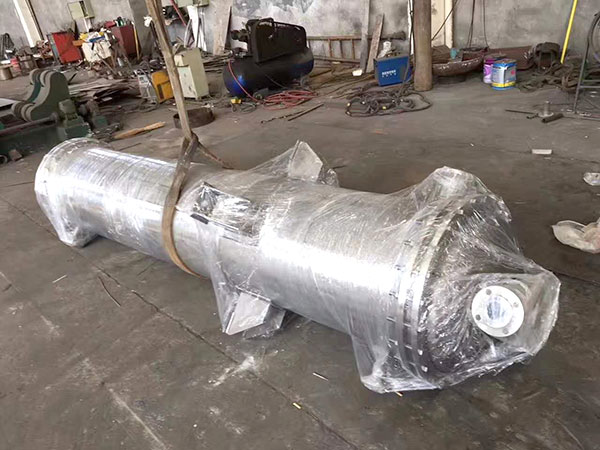
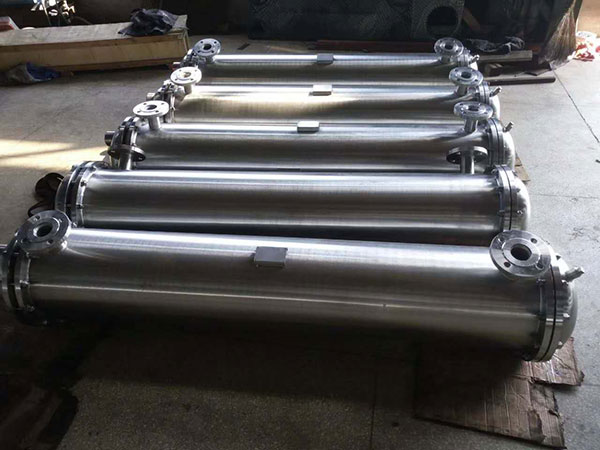
Tubular (also known as shell-and-tube and tube-and-tube) heat exchangers are the most typical dividing wall heat exchangers. They have a long history of application in industry and still occupy a dominant position among all heat exchangers. Tubular heat exchangers are mainly composed of shells, tube bundles, tube sheets and heads. The shells are mostly round in shape, with parallel tube bundles inside, and both ends of the tube bundle are fixed on the tube sheets.
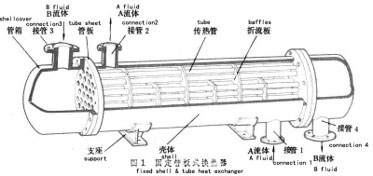
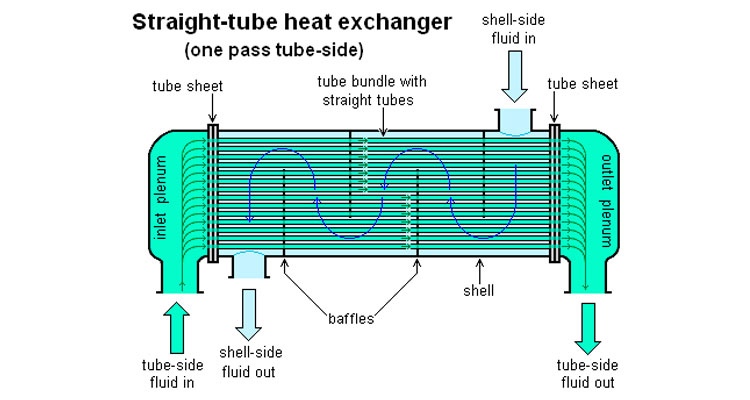
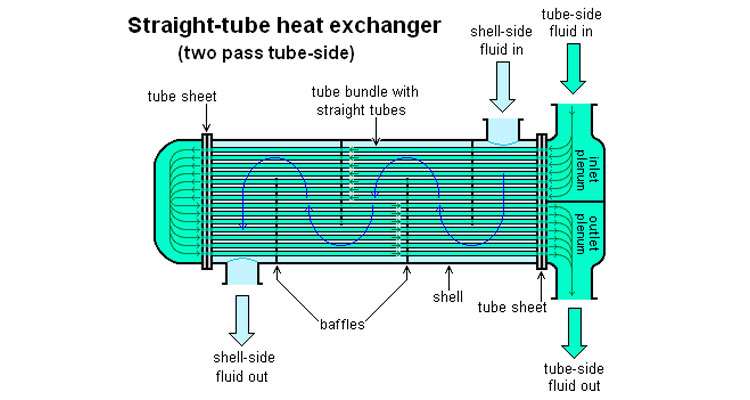
There are two kinds of fluids that exchange heat in a tubular heat exchanger. One flows inside the tube, and its stroke is called the tube side; the other flows outside the tube, and its stroke is called the shell side. The wall surface of the tube bundle is the heat transfer surface. In order to improve the heat transfer coefficient of the fluid outside the tube, a certain number of transverse baffles are usually installed in the shell. The baffles not only prevent the fluid from short-circuiting and increase the fluid speed, but also force the fluid to cross-flow through the tube bundle multiple times according to the prescribed path, greatly increasing the degree of turbulence. There are two commonly used baffles: round-shaped and disc-shaped, with the former being more widely used. Each time the fluid passes through the tube bundle in the tube is called a tube pass, and each time the fluid passes through the shell is called a shell pass. In order to increase the velocity of the fluid in the pipe, appropriate partitions can be installed in the heads at both ends to divide all the pipes into several groups evenly. In this way, the fluid can pass through only part of the tubes and return to the tube bundle multiple times at a time, which is called multi-tube pass. Similarly, in order to increase the flow rate outside the tube, longitudinal baffles can be installed in the shell to allow the fluid to pass through the shell space multiple times, which is called multi-shell pass. In a tubular heat exchanger, due to the different temperatures of the fluid inside and outside the tube, the temperatures of the shell and the tube bundle are also different.
The fixed tube plate heat exchanger has the tube plates at both ends directly welded to the shell. It is mainly composed of shell, tube plate, tube bundle, head and other main components. There is a tube bundle in the shell, and the two ends of the tube bundle are fixed on the tube plate by welding, expansion joint or a combination of expansion welding, and the outer periphery of the tube plate and the head flange are fastened with bolts. The fixed tube plate heat exchanger has a simple structure, low cost, easy manufacturing, and convenient tube side cleaning and maintenance. However, the shell side cleaning is difficult and there is temperature difference stress after the tube bundle is manufactured. When there is a large temperature difference between the heat exchange tube and the shell, the shell should also be equipped with an expansion joint.
The tube sheet at one end of the floating head heat exchanger is fixed between the shell and the tube box, and the tube sheet at the other end can move freely within the shell, which means that the shell and the tube bundle can expand freely. Therefore, there is no temperature difference stress between the tube bundle and the shell. Generally, the floating head is removable, and the tube bundle can be freely extracted and loaded. This structure of the floating head heat exchanger can be used in working conditions where there is a large temperature difference between the tube bundle and the shell. The cleaning and maintenance of the tube bundle and shell are relatively convenient, but its structure is relatively complex and the requirements for sealing are relatively high.
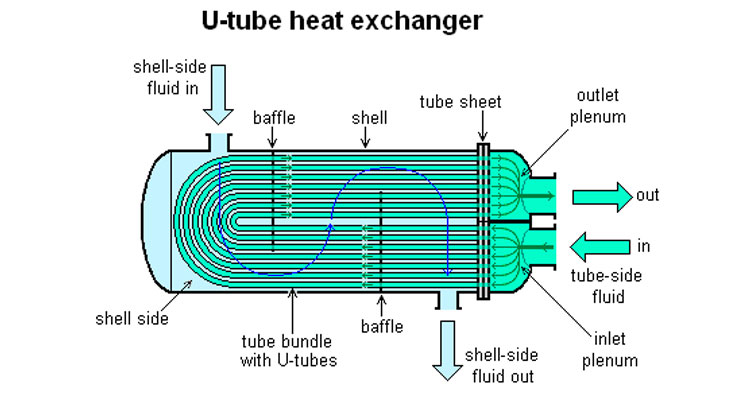
U-shaped tube heat exchanger is a heat exchange tube welded into a U shape, with both ends fixed on the same tube plate. Since the shell and heat exchange tubes are separated, the heat exchange tube bundle can expand and contract freely without causing temperature difference stress due to the temperature difference of the medium. The U-shaped tube heat exchanger has only one tube plate, no floating head, and its structure is relatively simple. The tube bundle can be freely pulled out and installed for easy cleaning, and has the advantages of a floating head heat exchanger. However, since the heat exchange tubes are made into U-shaped bends with different radii, the outermost heat exchange tube can be replaced after damage, and other tubes can be replaced. Damage can only block the pipe. At the same time, compared with the fixed tube plate heat exchanger, because the heat exchange tube is limited by the bending radius, there is a gap in the center of the tube bundle, and the fluid can easily short-circuit, affecting the heat transfer effect.



COMPANY PROFILE

Founded in 2010.Shanghai Jiangxing Chemical Equipment Co.,Ltd. is located in——Shanghai,China. We specialized in manufacturing series of plate heat exchangers, fully weldedheat exchangers,heat exchanger units, replacements of plates and gaskets,brazed plate heatexchangers. Our plate heat exchangers are quality reliable and equivalent to the products fromworld well-known manufacturers. We also supply high quality OEM heat exchanger gaskets( EPDM, NBR & VITON ) and heat exchanger plates(Stainless Steel, Titanium, Hastelloy ) forplate heat exchanger ordinary maintenance.
EXHIBITION & CUSTOMER

CERTIFICATES

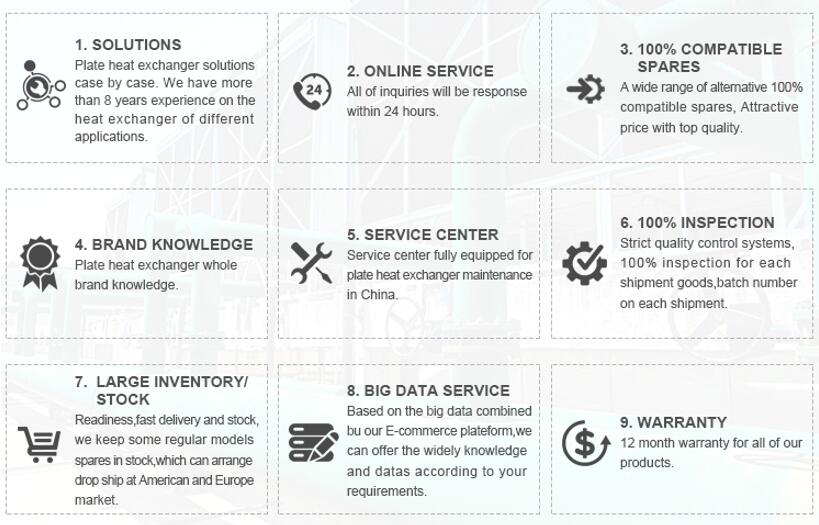
Why Choose Us
FAQ
1.Can l have your samples?
Yes, we can provide samples for you to check our quality.
2. What is your leading time for the products l need?
enerally 7 working days. lt depends on the quantities you request.
3.Do you have your own factory?
Yes, welcome to visit our factory and check our products.
4. What is the warranty for your products?
We provide one year warranty for all the items we sold.
5.What payment terms do you accept?
Trade Assurance/TT/ Letter of Credit/ Western Union












